
Other Subnet masks tell us the number of inhabitants that they can host in their neighborhoods, that is, the number of hosts. The formula always gives us the total number of hosts. The sum of the 0 values at hand is 24 bits. The element in determining the host numbers of subnet masks is that the sum of the 0 values available is found by the formula. Let’s take a look at how we reach these host number values The remaining 0 values give us the number of hosts we can use. You can see this more clearly in the table below, which is a summary of the host numbers of the subnet masks I have prepared above. Information: As the value of 255 falls within their class, the number of hosts they hosts increases.ġ1111111. Host Number of Subnet Masks, Host Calculation:Īs we go through step by step, before building our neighborhoods, let’s take a look at how many houses will be available in our neighborhoods, ie the number of hosts that can be accommodated in the network: Subnet Masks tell us how many houses will be located in a neighborhood when determining the neighborhoods of the houses, ie creating networks. These are the default subnet masks of their classes. So with the subnet mask, we do network partitions, which comes from the concept of subnetting. Every neighborhood child can only talk to those in their neighborhood, which is what is desired when building network structures. IP addresses the address of each house is Subnet Mask these are the structures that determine the neighborhoods of these houses. Now, let’s take a look at the Subnet Mask values according to the classes of these ips. I have given the IP ranges above that can be deployed in the LAN environment, ie inside. The IP limits and ranges outside the Private IP class and ranges mentioned above are the Public IP ranges and Public IP Ranges used in the WAN ( Wide Area Network ) environment, ie the external network. LAN environment, that can be distributed in the internal network IP Ranges ( Private IP ): To prevent this operation, it is important to use IPs in the private IP range that are set as a standard in the LAN environment. The reason for the two separate is that the IP addresses do not conflict with each other.

These IPs are divided into Public (Internet) and Private (LAN) IP addresses. These IP ranges from 1.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 are used in the Internet environment, ie the Public IP range. I will also use this logic when we move to the subnetting section.ġ26.255.255.255 IPs with 127 are used for testing purposes.
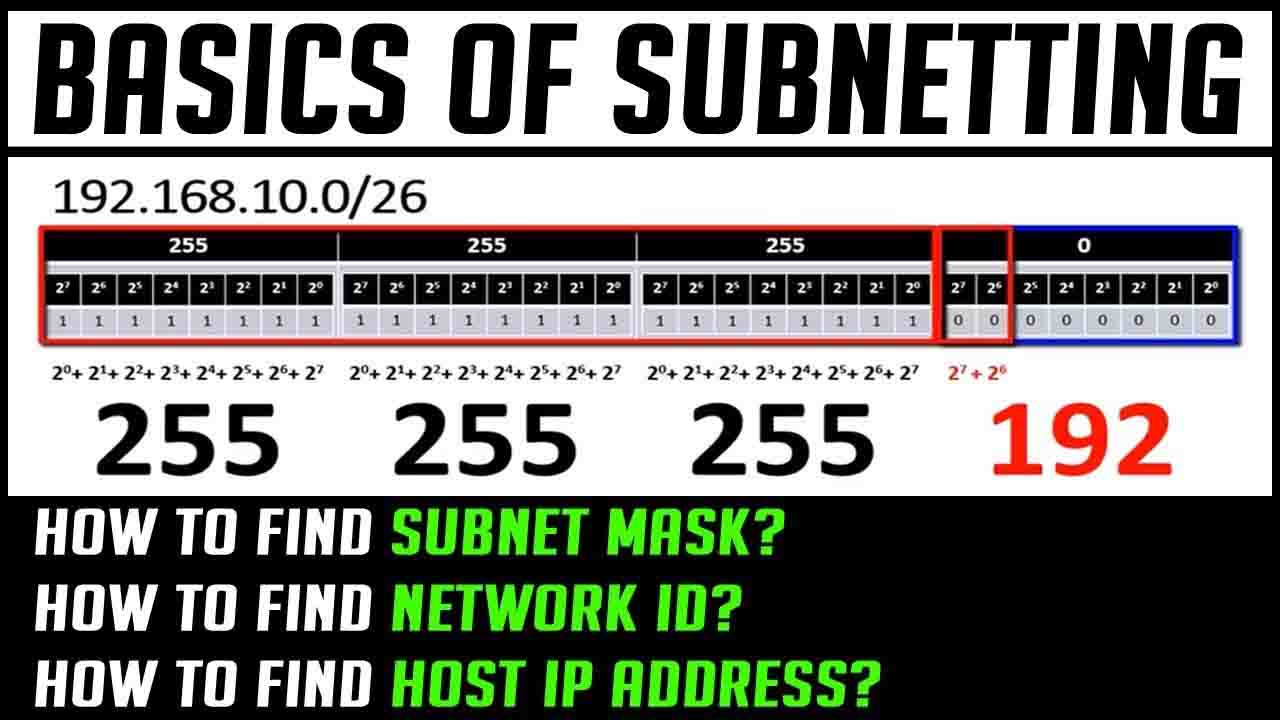
My reason for explaining this logic was to explain the logic of the IP addresses by which these values are obtained. If I set all 0 to 1, then I ‘ll have 255. I have obtained the value I want by summing the 1 value fields. Accordingly, the Binary equivalent of 192.168.20.10 Decimal Ip is as follows.The values of 1 corresponding to the values of 0 will be the parts we will add to the collection, which will give us the numerical equivalent on the corresponding Octet of the corresponding IP address.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
